
NEARLab is a collaborative research environment where biomedical, robotics, and computer science engineers work together to advance medical imaging, enhance robotic systems, and develop innovative medical robots.
We combine state-of-the-art technologies with innovative methodologies to advance research, collaborating closely with medical centers, industry partners, and academic institutions.
Continuum Robotics
Robotized applications for cardiovascular, neurovascular and endoluminal catheterized minimally invasive surgery
Design and Control
We focus on the design and control of continuum robots, characterized by flexible and deformable structures inspired by biological systems. Our methods enable smooth, safe, and dexterous motion in confined and sensitive environments.


Robot Modelling
We develop accurate mathematical and computational models to describe the kinematics and dynamics of continuum robots. These models are essential for control, sensing, and interaction, enabling reliable and predictable robot behavior.
Simulation and Planning
Our simulation and planning tools support the development and validation of continuum robotic systems. By predicting robot motion and interaction with the environment, we enable efficient path planning and reduce risks before deployment in real-world scenarios.

The Team
Contribute to this research line by
Robot Automation
We design autonomous robotic systems capable of planning, learning, and adapting to perform complex tasks reliably in dynamic environments.
Task and Motion Planning
We develop algorithms that enable robots to autonomously plan and execute complex tasks by coordinating high-level task reasoning with low-level motion control. These methods allow robots to operate robustly in dynamic and unstructured environments.


Learning-Based Control
Our learning-based control approaches leverage machine learning to improve robot performance through experience. By adapting to variability and uncertainty, these systems enable more flexible and resilient robotic behavior.
Adaptive Autonomy
We study adaptive autonomy to dynamically balance human involvement and robot independence. This allows robotic systems to adjust their level of autonomy based on task complexity, user intent, and environmental conditions.

The Team
Contribute to this research line by
Human-Robot Interaction
Algorithms and Framework for an enhanced collaboration paradigm between human and robots in the medical domain
Enhanced Surgical Robotics Training
We introduced Haptic Assistance algorithms into Virtual Reality environments used in the context of training robotics surgeons.
With an assisted training protocol, surgeons will undergo an impreved learning pathway that improves surgical performance and favors skill retention


Human-robot skills transfer
To release the complexity of surgical operations and reduce the workloads of surgeons, human-robot skill transferring is proposed to improve the practicability of surgical robots.
Learning the surgical skills from surgeon experts and reproduce these surgical operations is an effective way to enhance the autonomy of the surgical robot in RAMIS. Three stages are included in this process, namely, demonstration, learning, and reproduction.
Human-Robot shared control for Ultrasound Scanning
Ultrasound scanning benefits from a robotized approach in terms of reaching optimal resolution, 3D reconstruction and optimized force control
We embed an ultrasound probe on a robotic arm to execute a scanning procedure more effectively and with better results.

The Team
Contribute to this research line by
Mixed Reality
We leverage mixed reality technologies to enhance perception, interaction, and decision-making by seamlessly blending digital information with the physical world.
AR Surgical Navigation
We develop augmented reality systems for surgical navigation that overlay critical information directly onto the clinician’s view. This enhances spatial awareness, precision, and decision-making during complex procedures.


Intraoperative Guidance
Our AR-based intraoperative guidance solutions provide real-time visual cues and feedback during interventions. By integrating imaging, tracking, and patient-specific data, these systems support safer and more effective surgical workflows.
AR User Interface Design
We design AR user interfaces that are intuitive, ergonomic, and tailored to the needs of clinicians. Our focus is on minimizing cognitive load while maximizing clarity and interaction efficiency in high-stakes environments.

The Team
Contribute to this research line by
Computer Vision
Advanced image processing algorithms and artificial intelligence models to augment the information from medical images

3D Reconstruction of Surgical spaces
By exploiting the stereo capability of endosurgical cameras, we combine procedural disparity maps with modern deep learning models.
From this, we reconstruct the 3D surgical space from the 2D acquisitions in real-time, providing additional levels of information to the practitioner.
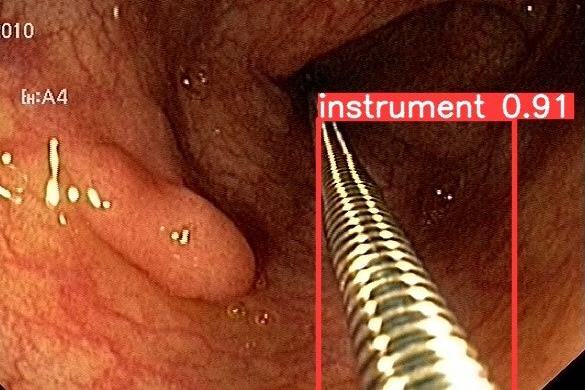
Semantic Segmentation of surgical instruments
By exploiting AI methods and learning capabilities, we propose innovative pipeline methods for object detection and segmentation.
From this, we obtain additional and innovative information, improving the modern approach to medical imaging.

Computer Vision Technologies for Computer-Assisted Fetal Therapies
Limited field of view (FoV), poor visibility, fetuses’ movements, high illumination variability and limited maneuverability of the fetoscope directly impact on the complexity of the surgery.
In the last decade, the medical field has seen a dramatic revolution thanks to the advances in surgical data science analysis such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) and in particular Deep Learning (DL).
The Team
Our Datasets are available for download
Contribute to this research line by
Predictive Medicine
We develop data-driven and AI-based methods to anticipate clinical events, support early diagnosis, and enable personalized and preventive healthcare.
Federated Learning
We apply federated learning techniques to enable collaborative model training across distributed clinical data sources while preserving data privacy. This approach allows robust and scalable learning without sharing sensitive patient data.


Explainable AI for Diagnosis
We develop explainable AI methods that provide transparent and interpretable insights into diagnostic decisions. These techniques support clinical trust, regulatory compliance, and informed decision-making by healthcare professionals.
Data-Driven Prediction of Clinical Events
Our data-driven models analyze multimodal clinical data to predict adverse events and disease progression. By enabling early detection and personalized risk assessment, these approaches support proactive and preventive healthcare

The Team
Contribute to this research line by

Find Us
NEARLab is located inside the Leonardo Robotics Labs space at Politecnico di Milano, piazza Leonardo da Vinci 32, Building 7, 20133, Milano, Italy
and at Campus Colombo in Via Giuseppe Colombo, 40, 20133 Milano MI
Hours
Monday to Friday: 8.00 A.M. – 20.00 P.M.
More
Website Maintainers
Benjamin Fortuno, Matteo Di Mauro, Alessandra Maria Trapani
Search
Get in touch
or visit the Research Areas and contact the corresponding team directly
Connections
Materials

