
NEARLab is a collaborative research environment where biomedical, robotics, and computer science engineers work together to advance medical imaging, enhance robotic systems, and develop innovative medical robots.
We combine state-of-the-art technologies with innovative methodologies to advance research, collaborating closely with medical centers, industry partners, and academic institutions.

Computer Vision
Advanced image processing algorithms and artificial intelligence models to augment the information from medical images

3D Reconstruction of Surgical spaces
By exploiting the stereo capability of endosurgical cameras, we combine procedural disparity maps with modern deep learning models.
From this, we reconstruct the 3D surgical space from the 2D acquisitions in real-time, providing additional levels of information to the practitioner.
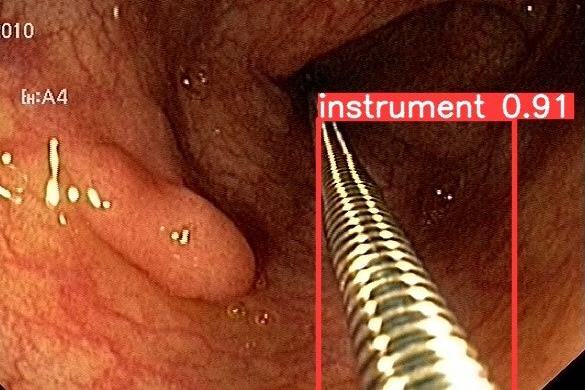
Semantic Segmentation of surgical instruments
By exploiting AI methods and learning capabilities, we propose innovative pipeline methods for object detection and segmentation.
From this, we obtain additional and innovative information, improving the modern approach to medical imaging.

Computer Vision Technologies for Computer-Assisted Fetal Therapies
Limited field of view (FoV), poor visibility, fetuses’ movements, high illumination variability and limited maneuverability of the fetoscope directly impact on the complexity of the surgery.
In the last decade, the medical field has seen a dramatic revolution thanks to the advances in surgical data science analysis such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) and in particular Deep Learning (DL).
Under-XAI
Understanding Ovarian Cancer initiation and progression through Explainable Artificial Intelligence.
We develop an explainable AI-driven decision-support system for assisting the clinicians in making well-informed diagnosis and therapy decisions, ultimately leading to improved treatment outcomes for patients affected by ovarian cancer.
Partners
IEO: Istituto Europeo di Oncologia (Milan, IT) – Università degli studi Magna Graecia (Catanzaro, IT) – Azienda Ospedaliero-Universitaria di Cagliari (Cagliari, IT) – Università degli studi dell’Insubria (Varese, IT)

CAL.HUB.RIA
The project “CAL.HUB.RIA” (CALabria HUB for Innovative and Advanced Research), included in the Health Operational Plan, focuses on two main activities: The development of a platform for collecting and harmonizing data on rare diseases; The implementation of machine learning models to support clinical decision-making in patients with advanced-stage brain gliomas (glioblastoma).
TIMECARE
The objective of the TIMECARE project is to develop artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms that can analyse biosignals to predict cardiovascular events and facilitate early recognition. The project will also develop AI algorithms to analyse videos to detect out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA) and augmented reality (AR) methods to deliver patient-specific cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and defibrillation. The ultimate goal is to reduce mortality and disability.

The Team
Our Datasets are available for download
Contribute to this research line by

Soft Robotics
Robotized applications for cardiovascular, neurovascular and endoluminal catheterized minimally invasive surgery

ARTERY is a radiation-free approach based on shared-autonomy robotic catheters, with increased user engagement and easy interaction.
The fusion of the information yielded by echocardiography, optical and electromagnetic sensing techniques will provide a superior view upon the cardiovascular space.
Fluidic actuation paired with artificial intelligence will be the pillars motors of the next generation of robotic catheters that autonomously find their way towards the target site.
Through a fully immersive augmented reality interface, the operator will monitor the intravascular route of the catheter with no need for radiation-based imaging
Partners
Sant’Anna University (Pisa, IT) – KU Leuven (Leuven, BE) – IRCCS San Raffaele Hospital (Milano, IT) – SwissVortex (Zürich, SW) – Artiness (Milano, IT) – FBGs (Jena, GE)
ATLAS develops smart flexible robots that autonomously propel through complex deformable tubular structures. This calls for seamless integration of sensors, actuators, modelling and control.
By engaging in this ambitious research topic, participants will be exposed to all aspects of robotics. While contributing to the state of the art, they will become proficient in building, modelling, testing, interfacing in short in integrating basic building blocks into systems that display sophisticated behavior.

Partners
KU Leuven (Leuven, BE) – Sant’Anna School of Advanced Studies (Pisa, IT) – University Of Verona (Verona, IT) – University of Strasbourg (Strasbourg, FR) – Delft University of Technology (Delft, NE) – Polytechnic University of Catalonia (Barcelona, SP)

DIH-HERO’s primary objective is to accelerate innovation in robotics for healthcare.
To connect innovators, providers, businesses, users and politicians, DIH-HERO will establish an open online portal offering multiple services facilitating collaboration on various innovations, emphasizing the sharing of best practice and enhancing the delivery of innovation throughout the value chain.
DIH-HERO especially focuses on supporting small and medium-sized enterprises in maximizing their impact and reducing time-to-market
Partners
Sant’Anna University (Pisa, IT) – Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia (Genova, IT) – Universiteit Twente (Twente, NE) – University Hospital RWTH Aachen (Aachen, GE) – Fraunhofer Institute for Manufacturing Engineering and Automation (Stuttgart, GE) – Imperial College (London, UK) – Danish Technological Institute (Taastrup, DE), ETH (Zurich, SW)
The Team
Contribute to this research line by

Human-Robot Interaction
Algorithms and Framework for an enhanced collaboration paradigm between human and robots in the medical domain
Enhanced Surgical Robotics Training
We introduced Haptic Assistance algorithms into Virtual Reality environments used in the context of training robotics surgeons.
With an assisted training protocol, surgeons will undergo an impreved learning pathway that improves surgical performance and favors skill retention


Human-robot skills transfer
To release the complexity of surgical operations and reduce the workloads of surgeons, human-robot skill transferring is proposed to improve the practicability of surgical robots.
Learning the surgical skills from surgeon experts and reproduce these surgical operations is an effective way to enhance the autonomy of the surgical robot in RAMIS. Three stages are included in this process, namely, demonstration, learning, and reproduction.
Human-Robot shared control for Ultrasound Scanning
Ultrasound scanning benefits from a robotized approach in terms of reaching optimal resolution, 3D reconstruction and optimized force control
We embed an ultrasound probe on a robotic arm to execute a scanning procedure more effectively and with better results.


REDIT – Robot-assisted Remote Echography for Diagnosis and Treatment
The REDIT project aims to empower ultrasound specialists to perform remote diagnostic exams, addressing challenges in isolated or mobile settings lacking on-site specialists. The core objectives encompass:
1) the development of a shared-autonomous robotic ultrasound scanning system, with embedded AI-enabled techniques to guide the transducer and avoid missing suspicious regions
2) the refinement of augmented interfaces, i.e., Augmented Reality (AR), to enhance the ergonomics and efficacy of remote ultrasound-guided diagnosis and interventions
3) a rigorous health technology assessment, emphasizing system transparency and usability through extensive validation on phantom models.
The Team
Contribute to this research line by

Find Us
NEARLab is located inside the Leonardo Robotics Labs space at Politecnico di Milano, piazza Leonardo da Vinci 32, Building 7, 20133, Milano, Italy
and at Campus Colombo in Via Giuseppe Colombo, 40, 20133 Milano MI
Hours
Monday to Friday: 8.00 A.M. – 20.00 P.M.
More
Website Maintainers
Alberto Rota, Mattia Magro, Alessandra Maria Trapani
Search
Get in touch
or visit the Research Areas and contact the corresponding team directly
Connections
Materials


